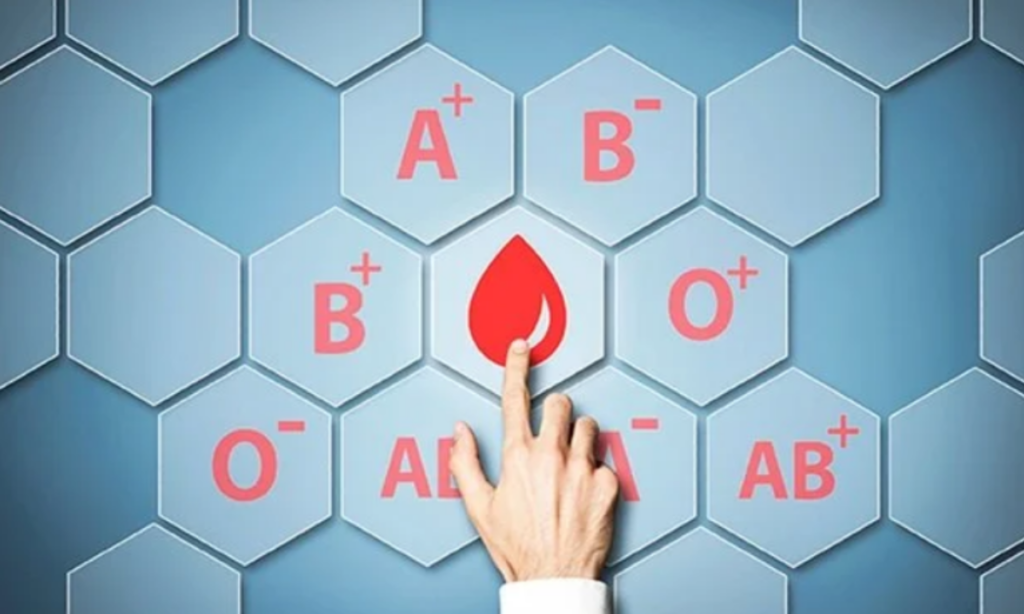

Understanding the Link Between Blood Type and Health
Do you know your blood type? Surprisingly, millions of people around the world do not. However, scientific research suggests that blood type may play an important role in overall health, influencing the risk of developing certain medical conditions. Blood type is genetically inherited and determined by the presence of specific antigens on red blood cells.
Understanding how blood type affects the body can provide valuable insight into disease prevention and long-term wellness.
The ABO Blood Group System
The ABO blood group system, developed by Nobel Prize–winning scientist Dr. Karl Landsteiner, is the primary classification method used worldwide. This system categorizes blood based on the presence or absence of antigens A and B found on red blood cells and within plasma antibodies.

There are four main blood types:
Type A
Type B
Type AB
Type O
Blood types are also classified by the Rh factor. If red blood cells contain the Rh antigen, the blood type is Rh-positive. If the antigen is absent, the blood type is Rh-negative.
Why Knowing Your Blood Type Is Important
Knowing your blood type is essential for medical safety, particularly during blood transfusions. Doctors must ensure compatibility to prevent dangerous immune reactions.

According to Dr. Guggenheim of the Abramson Cancer Center, antigens trigger immune responses when the body encounters unfamiliar substances. If incompatible blood is transfused, red blood cells can clump together, potentially leading to severe or fatal complications.
Blood typing involves mixing a sample with anti-A and anti-B antibodies to observe reactions. Individuals with Type O blood, which lacks A and B antigens, are considered universal donors.
Blood Type and Heart Disease Risk

Scientific studies published by the American Heart Association have linked certain blood types to higher cardiovascular risk.
People with Type A, B, or AB blood face:
8% higher risk of heart attack
10% higher risk of heart failure
51% greater risk of deep vein thrombosis
47% higher risk of pulmonary embolism
These findings suggest that individuals in these groups should pay closer attention to heart health and circulation.
Blood Type and Memory Problems
Research indicates that individuals with Type AB blood may be more vulnerable to memory and cognitive decline in later life. Although this blood type represents only about 4% of the population, studies show that people with Type AB blood are 82% more likely to develop dementia-related memory issues compared to other blood types.
Blood Type and Stomach Cancer Risk
Gastric cancer is the fifth most commonly diagnosed cancer and the third leading cause of cancer-related death worldwide.
Studies show that individuals with Type A, B, or AB blood have a higher risk of developing stomach cancer compared to those with Type O blood. Type A blood carries the highest risk, largely due to increased susceptibility to Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) infections bacteria that cause stomach inflammation, ulcers, and long-term damage.
Ulcers and Type O Blood
Although Type O blood offers some protection against gastric cancer, it is associated with a higher risk of peptic and duodenal ulcers. Research suggests that H. pylori bacteria bind more easily to the stomach lining of individuals with Type O blood, increasing ulcer formation.
Final Thoughts
While blood type alone does not determine your health, it provides important clues about potential risks. Knowing your blood type can help guide preventive care, improve medical decision-making, and encourage healthier lifestyle choices.
Understanding your blood type means gaining deeper insight into how your body works and how to protect it.